Introduction
The worldwide 5G subscriptions are expected to exceed 3.4 billion by 2026, with North America, Western Europe and North East Asia leading the pack. The rapid expansion of 5G networks will significantly change the current roaming process. The new relationships between Digital Service Providers (DSPs) and enterprise networks will become more complex than ever before. The contract negotiation, management, and reconciliation of inter-operator agreements will become more challenging, especially when it comes to ensuring an accurate clearing and settlement of transactions among a complex network of roaming partners. Incorrect identification of roaming data can increase revenue leakage and impact the business.
A possible solution to thrive in the 5G economy is adopting blockchain-enabled roaming service activation and dispute settlement. Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network. A blockchain-enabled roaming service would make the entire process more automated and robust while ensuring greater transparency, accuracy, and security in all roaming transactions.
Challenges faced by DSPs in the current roaming process and how this complexity will further increase with the onset of 5G and IoT
- Increased number of players in the 5G and IoT ecosystem and the launch of new products and offerings will lead to a multi-fold increase in contracts and disputes
- 5G unlocks a world of opportunities enabling varied services like connected cars, smart grid, virtual and augmented reality, and a wide array of internet of things (IoT) applications. Gradually these services will be bundled and offered to roamers as well. This will make the roaming services more complicated as the service orchestration and billing will be further extended to other systems involving multiple players in the ecosystem. Along with the service providers and end customers, this would also include OEMs, software vendors, cloud providers and many more. These multi-party transactions are governed and controlled by various manual contracts bound by multiple rules. In turn, these 5G enabled services will lead to a multi-fold increase in contracts and disputes.
- Providing roaming service in an ecosystem where both 4G and 5G network co-exists will further complicate the service activation process
- The 5G network brings two types of network operations to serve the existing 4G and the new 5G deployment. The Non-Standalone (NSA) mode works on both 4G and 5G networks and the Standalone (SA) mode works on a dedicated 5G network. As the deployment effort of a standalone mode is significantly higher in terms of Capex and Opex, it will take longer to get settled in the new ecosystem. Hence, the non-standalone mode will be the path of transition. However, this will complicate the key roaming processes such as latching to visiting network, user authentication and billing settlements.
- Complex contract management with multiple systems decreases the overall process efficiency
- Currently, DSPs need to maintain the contract management information on multiple systems and in some cases, it may even be spreadsheets. This leads to redundant provisioning, longer onboarding, and tedious service activation processes. It increases the risk of missed or misaligned configuration amongst multiple service instances. As the market complexity grows in the 5G era, the contracts often lead to complex and incorrect calculations, resulting in commitment penalties and unnecessary costs due to improper management.
- Delayed dispute settlement impacts the cash flows
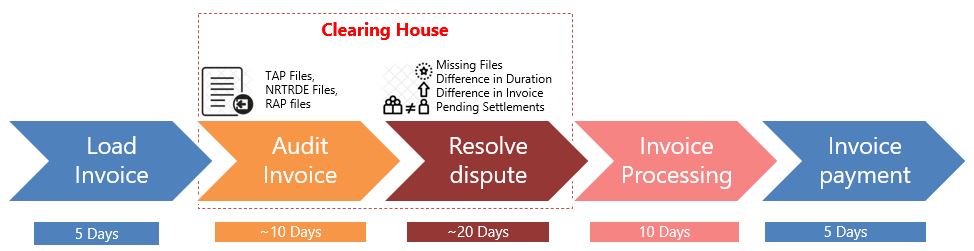
Fig 1: A typical workflow of dispute settlement through the clearing house
- The evolution of competitive markets naturally increases the number and type of disputes. These may involve failures to fulfil contractual obligations, non-compliance with regulatory requirements, and a wide range of other issues. Settling the disputes with the current approach often takes several months. The primary reason for this delay is the dependency on the clearing house. The clearing house audits the bills and the required artefacts against the agreed contracts. This process is tedious, repetitive, and semi-automatic. It follows a multi-level approval workflow that leads to a longer settlement time. Also, the reconciliation process is maintained in a ledger, making it vulnerable to fraudulent activities and creating trust issues.
Adopting blockchain-enabled roaming service activation and dispute settlement can enable DSPs to thrive in the 5G economy
The intrinsic properties of blockchain can revolutionize the process of service activation and dispute settlement in the 5G era. It drives a faster settlement process and minimal revenue leakage. Additionally, it provides a robust platform to monetize the new business opportunities from 5G and IoT.
Fig 2: Intrinsic properties of Blockchain Technology
Use Case 1 – Blockchain-enabled roaming service activation
Due to the use of multiple systems, the traditional service activation process undergoes a tedious backend operation. The inconsistent record of service activation often leads to various frauds such as sim cloning and identity theft.
Blockchain enables decentralized data processing and secure transactions, removing the need for maintaining multiple systems, simplifying the entire service activation process, and ensuring inter-party operations run more smoothly. It ensures that:
- All the partners and operators (Home operator and Visiting operator) are part of a blockchain consortium (i.e., a permissioned network)
- All business logics like contract validation for different countries, ID validation and subscription validations are done through smart contracts (a software program that is intended to automatically execute, control or document legally relevant events and actions when predetermined conditions are met)
- Operators either choose a mechanism where any monetary transactions can be done between the operators through the inbuilt wallet, or they can choose to keep it out of blockchain like the traditional one
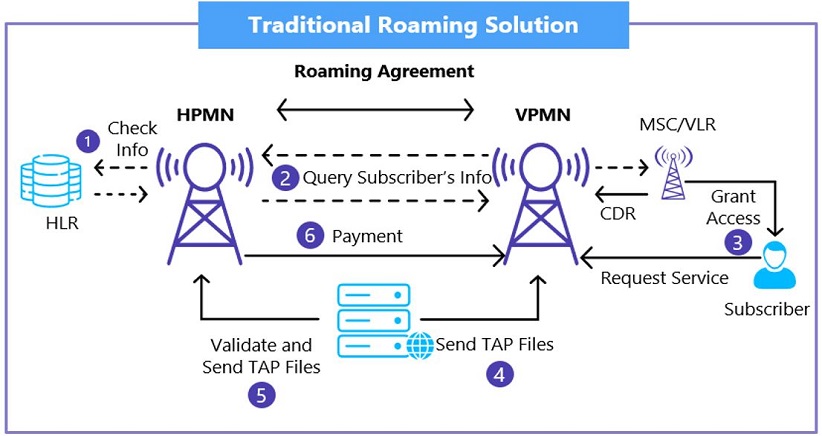
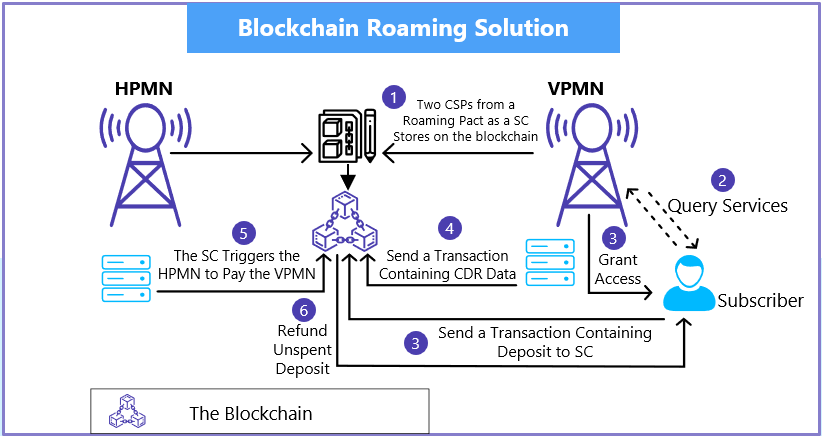
Fig 3: The Blockchain-enabled roaming solution, with its inbuilt capability of decentralized data processing and secure transactions, removes the need for maintaining multiple systems, simplifies the entire service activation process and ensures interparty operations are done more smoothly
Legend:
- HLR – Home location Register
- HPMN – Home Public Mobile network
- VPMN – Visiting Public Mobile network
- MSC – Mobile switching Center
- VLR – Visiting Location Register
- CDR- Call detail record
- TAP- Telecom application Protocol
- SC- Switching Center
Let’s see an example of the blockchain-enabled roaming solution. If the subscriber agrees to use the roaming service, he sends a request to consume the service. To enable this, a smart contract is executed that checks if the subscriber is legitimate. Once this is established, the subscriber can use the services in the visiting network. After the subscriber ends the roaming service, the visiting network (VPMN) sends the transaction details to the home network (HPMN), which consists of the CDR data of the provided service. The smart contract then calculates the subscriber’s service fee and triggers a transaction for payment of the services. All these steps are completely transparent, instantaneous, and automated using blockchain, which removes the chances of any fraudulent activities.
In the traditional roaming process, a subscriber cannot avail the visiting location’s exclusive services and subscriptions. This is due to limitations/absence of various agreements, near real-time sharing of XDRs, and faster settlements between the partner networks. However, the smart contract resolves complicated contract management processes, facilitates faster settlements between the partners and at the same time stores the data in a decentralized manner for easier consumption in the future.
Use Case 2 – Blockchain-enabled automatic dispute settlements
The settlement process enabled by blockchain tackles three difficult and time-consuming processes in the settlement lifecycle – audit invoice, resolve dispute, and invoice processing. The immutable distributed ledger removes the dependencies on intermediaries and makes the entire process more automatic and robust. This brings down the entire settlement duration from few months to just a few days.
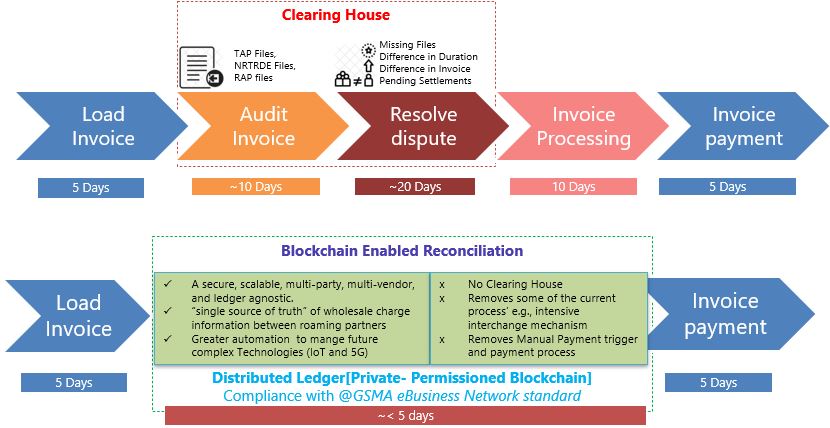
Fig 4: Blockchain-enabled automatic dispute settlements
As a prerequisite, all the partners must agree to the principles and be part of the blockchain network. This establishes trust between various parties as it prohibits unilateral changes in the process.
Once the settlement process is initiated, various smart contracts (from the blockchain) are triggered to check the inputs and conditions as per the agreements. This significantly improves the collections of XDRs in near real-time, and hence the billing generation becomes more accurate, resulting in faster settlements and decreased revenue leakage.
Conclusion
Blockchain can completely revolutionize the roaming service activation and dispute settlement processes. For DSPs, the value realization will increase exponentially once the 5G is fully functional along with various IoT-enabled services. Adopting blockchain earlier can enable DSPs to easily tap new business opportunities, have more viable ways to manage their business, and launch new services much faster with a reduced total cost of ownership.